What Is Ozone Therapy: Immune-Boosting Oxygen Treatment
 By Dr. Justin Marchegiani
By Dr. Justin Marchegiani
What is Ozone Therapy?
Ozone (O₃) is a naturally occurring gas of three oxygen atoms. It exists in the Earth's atmosphere, forming a protective layer that shields us from harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, ozone can offer remarkable health benefits when harnessed in controlled therapeutic doses.
Ozone therapy administers medical-grade ozone gas into the body through various methods to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and combat pathogens.
How Ozone Therapy Works
Ozone is a potent oxidant that triggers oxidative stress when introduced into the body. Although oxidative stress is typically associated with cell damage, it stimulates the body’s natural defense mechanisms in therapeutic doses.
Here’s how it works:
- Pathogen Destruction: Ozone directly damages and destroys bacteria, viruses, and fungi by breaking down their cell walls and membranes.
- Cellular Oxygenation: It enhances oxygen delivery to cells, improving cellular respiration and energy production.
- Immune Modulation: Ozone therapy stimulates the immune system by activating white blood cells, which helps the body fight infections and reduce inflammation.
Key Benefits of Ozone Therapy
✅ 1. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties
Ozone therapy is highly effective in destroying harmful pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- How it works: The ozone molecule penetrates bacterial and fungal cell walls, oxidizing and destroying lipids, proteins, and DNA, ultimately killing the microorganism.
- Biofilm Breakdown: Ozone can break down biofilms, which are protective layers that bacteria use to shield themselves from antibiotics. This makes ozone therapy particularly valuable for chronic or antibiotic-resistant infections.
✅ 2. Immune System Modulation
Ozone therapy has a unique ability to balance the immune system:
- Overactive Immune System: In cases of autoimmune diseases, ozone therapy can reduce excessive immune responses and inflammation.
- Weak Immune System: For individuals with chronic infections or weakened immunity, ozone therapy stimulates immune activity, improving the body’s ability to fight off pathogens.
✅ 3. Antioxidant Boosting
Ozone therapy increases the production of endogenous antioxidants, including:
- Glutathione: A powerful antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress and detoxifies cells.
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD): Protects against cellular damage caused by free radicals.
- Catalase: Enhances the body’s natural detoxification processes.
✅ 4. Increased Oxygen Efficiency
Ozone enhances the body's oxygen utilization, which can be especially beneficial for individuals with:
- Diabetes: Improved oxygenation enhances circulation and tissue repair, reducing the risk of diabetic ulcers and promoting faster wound healing.
- Chronic fatigue or fibromyalgia: Better oxygen delivery may reduce fatigue and enhance cellular energy production.
✅ 5. Improved Circulation
By increasing blood flow, ozone therapy enhances oxygen delivery to tissues, making it valuable for individuals with:
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- Chronic inflammation
- Poor circulation due to diabetes or cardiovascular issues
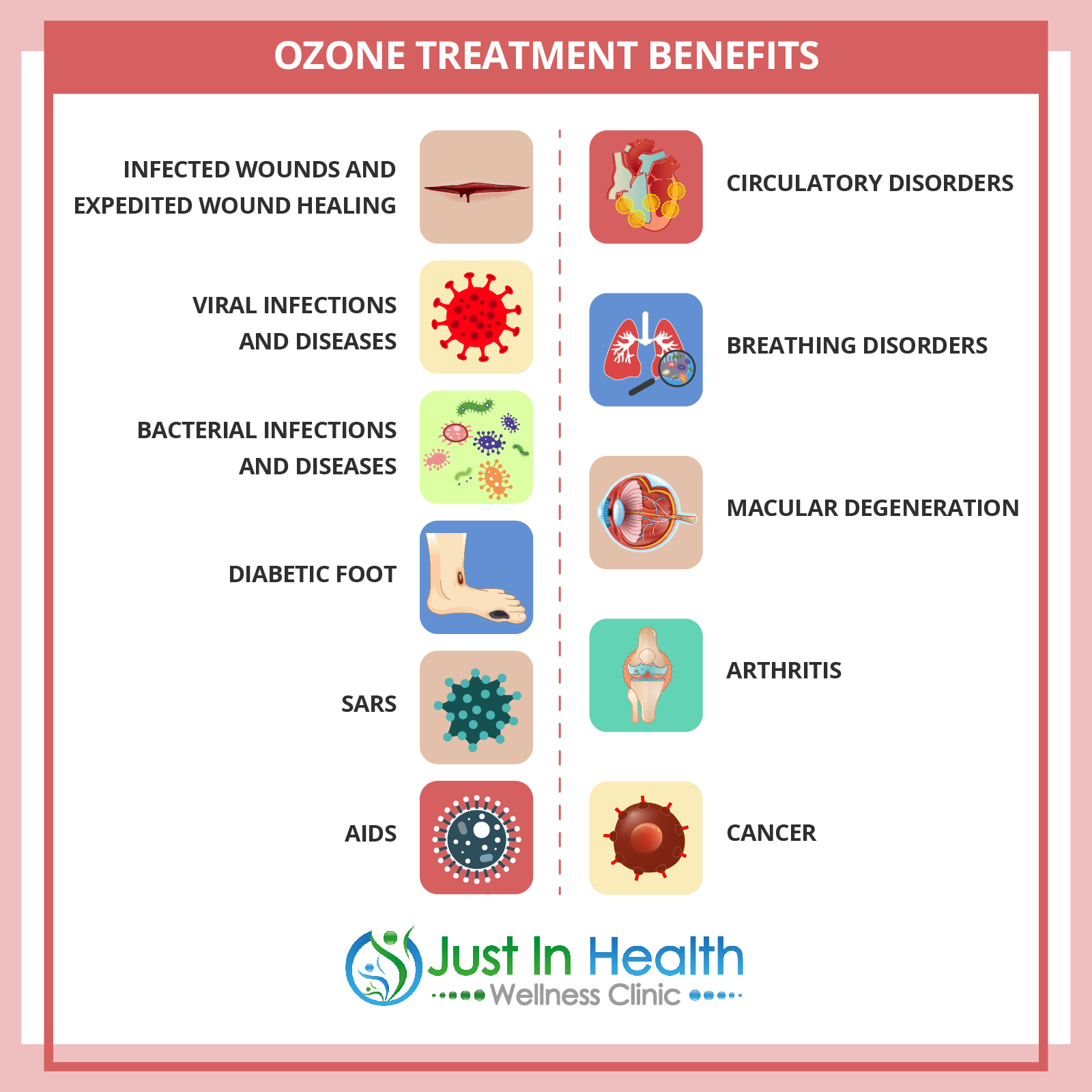
Conditions That May Benefit from Ozone Therapy
Ozone therapy has shown promise in treating a wide range of conditions, including:
- Chronic Infections: Lyme disease, hepatitis, and chronic sinus infections.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS): Boosts energy by enhancing cellular oxygenation.
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Improves wound healing and prevents infection.
- Cardiovascular Disorders: Enhances blood flow and oxygen delivery.
- Respiratory Conditions: Improving oxygenation may help individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
- Joint Pain and Arthritis: Reduces inflammation and relieves pain.
Administration Methods of Ozone Therapy
Ozone therapy can be administered in various ways, depending on the condition being treated:
💉 1. Auto-Hemotransfusion
- Blood is drawn from the patient, mixed with ozone gas, and then reinfused into the body.
- It is commonly used for chronic infections, autoimmune diseases, and immune modulation.
🌬️ 2. Ozone Insufflation
- Rectal Insufflation: Ozone gas is introduced through the rectum, where it is absorbed by the intestines and enters the bloodstream.
- Vaginal Insufflation: Used for gynecological infections.
💧 3. Ozone Water Ingestion
- Ozone gas is dissolved into water and consumed orally.
- Used for gut infections and gastrointestinal issues.
🩸 4. Ozone Injection
- Ozone gas is directly injected into joints or tissues.
- Used for pain management and joint inflammation.
🌿 5. Topical Ozone Therapy
- Ozone gas is applied directly to the skin using a sealed bag or chamber.
- It is commonly used for wound healing and skin infections.
Potential Risks and Safety Precautions

While ozone therapy offers many potential benefits, it carries some risks:
- Ozone Toxicity: Inhalation of ozone gas can irritate the lungs and cause respiratory issues.
- Oxidative Stress: Excessive ozone exposure can overwhelm the body’s antioxidant defenses, leading to cell damage.
- Lack of FDA Approval: Ozone therapy is not currently FDA-approved in the United States, making it difficult to access through conventional healthcare channels.
✅ Safety Tips
- Ensure therapy is administered by a qualified healthcare provider.
- Avoid inhaling ozone directly.
- Start with low doses and gradually increase as tolerated.
Why Ozone Therapy Needs More Research
Despite its promising effects, ozone therapy remains under-researched due to:
- Lack of Large-Scale Clinical Trials: Most current studies are small and lack FDA validation.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Influence: Ozone therapy offers a low-cost alternative to expensive drugs, making it less profitable and, therefore, less promoted.
- Safety Concerns: Further research is required to establish optimal dosages and minimize potential risks.
✅ Conclusion
Ozone therapy offers many potential health benefits, from combating chronic infections to improving circulation and boosting immune function. Although it is not yet FDA-approved, many functional medicine practitioners successfully use it as an alternative treatment for chronic conditions.
While more clinical research is needed, ozone therapy holds promise as a powerful tool in integrative and functional medicine.
💡 FAQs
1. Is ozone therapy safe?
Ozone therapy is generally safe when administered by a trained professional. However, improper use or excessive exposure can lead to side effects.
2. How many sessions are required for ozone therapy to be effective?
The number of sessions varies depending on the condition being treated. Chronic conditions may require multiple sessions over several weeks.
3. Is ozone therapy legal in the United States?
While ozone therapy is not FDA-approved, it is legally administered by some functional and alternative medicine practitioners.
4. Can ozone therapy help with chronic Lyme disease?
Ozone therapy is often used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for chronic Lyme disease due to its antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties.
5. What are the side effects of ozone therapy?
Potential side effects include fatigue, headaches, or mild flu-like symptoms, usually temporary.
References:
- Bocci, V. (2011). Ozone: A New Medical Drug. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Elvis, A. M., & Ekta, J. S. (2011). Ozone therapy: A clinical review. Journal of Natural Science, Biology, and Medicine, 2(1), 66–70. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-9668.82319
- Clavo, B., Santana-Rodríguez, N., Llontop, P., et al. (2018). Ozone therapy as adjuvant for cancer treatment: Is further research warranted? Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2018, 7931849. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7931849
- Rowen, R. J., & Robins, H. (2019). A plausible “penny” costing effective treatment for corona virus—Ozone therapy. Medical Gas Research, 9(3), 109-110. https://doi.org/10.4103/2045-9912.267703
- Carpendale, M. T., & Freeberg, J. K. (1991). Ozone inactivates HIV at noncytotoxic concentrations. Antiviral Research, 16(3), 281-292. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-3542(91)90045-S
- Schwartz, S. (2016). Ozone therapy in diabetic foot: Clinical case report. Clinical Case Reports, 4(6), 602-604. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.593
- Viebahn-Haensler, R., & León Fernández, O. S. (2021). Ozone in medicine: The low-dose ozone concept—Guidelines and mechanisms of action. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1765(1), 012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1765/1/012011
- Re, L., Sánchez, G. M., & Mawsouf, M. N. (2011). Oxygen-ozone therapy in medicine: An update. Infectious Disorders – Drug Targets, 11(2), 150-161. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152611795589895
- Martínez-Sánchez, G., Al-Dalain, S. M., Menéndez, S., et al. (2005). Therapeutic efficacy of ozone in patients with diabetic foot. European Journal of Pharmacology, 523(1-3), 151-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.033
- Smith, C. M., & Bisht, G. (2019). Ozone therapy: A review of current applications and future directions. Frontiers in Public Health, 7, 309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00309

 By Dr. Justin Marchegiani
By Dr. Justin Marchegiani
