
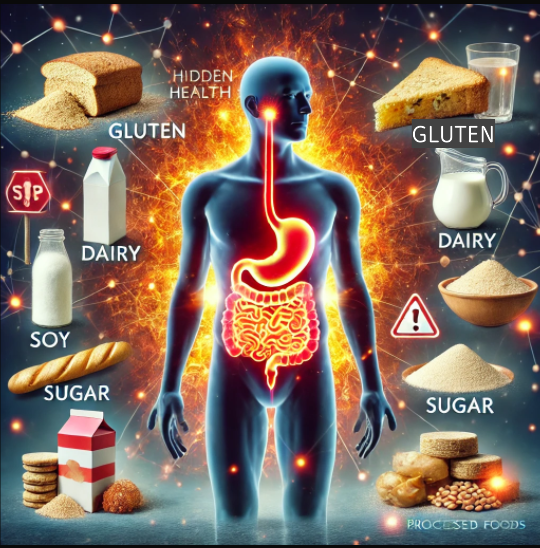
If you’ve been dealing with persistent health issues like fatigue, digestive problems, joint pain, brain fog, or skin conditions without clear answers, hidden inflammation could be the root cause. One of the most significant contributors to chronic inflammation is food sensitivities—subtle yet harmful reactions to everyday foods that quietly wreak havoc on your body over time.
Unlike food allergies, which trigger immediate and severe reactions, food sensitivities cause low-grade inflammation that can last for days or even weeks. This ongoing immune response weakens your gut lining, disrupts your body’s balance, and can eventually lead to autoimmune conditions and other chronic health problems.
In this article, we’ll explore the connection between food sensitivities and inflammation, identify the most common inflammatory foods, and provide actionable strategies to detect and eliminate problem foods—helping you reclaim your health and vitality.
Your immune system’s job is to protect you from harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and toxins. However, when it mistakenly sees certain foods as a threat, it launches an inflammatory response that can damage your tissues over time.
One of the key factors in food sensitivities is leaky gut syndrome—a condition where the gut lining becomes overly permeable. Normally, the gut acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to pass into your bloodstream while keeping harmful substances out.
However, factors like stress, processed foods, toxins, medications, and infections can weaken this barrier, allowing undigested food particles to escape into the bloodstream. Your immune system sees these particles as foreign invaders and triggers an inflammatory response.
If these symptoms sound familiar, your body might be reacting to certain foods—causing low-grade, chronic inflammation that wears down your health over time.
Certain foods are more likely to trigger immune reactivity, especially if you already have gut imbalances or a history of digestive issues.
If you suspect food sensitivities, avoiding these common triggers could significantly reduce inflammation and improve your overall health.
If you’re experiencing symptoms but don’t know which foods are causing issues, there are several ways to uncover hidden food sensitivities.
An elimination diet is the most effective way to identify food sensitivities. It involves removing common inflammatory foods for several weeks and then reintroducing them slowly while tracking your body’s reactions.
✔ Phase 1 – Eliminate: Remove gluten, dairy, soy, corn, eggs, nightshades, sugar, and processed foods for at least 3–6 weeks.
✔ Phase 2 – Reintroduce: Add one food back every 3–4 days while noting any symptoms.
✔ Phase 3 – Maintain: Avoid foods that trigger symptoms and focus on eating whole, nutrient-dense foods.
This method requires patience, but it is the most accurate way to pinpoint food sensitivities.
There are lab tests that measure IgG and IgA antibody reactions to foods. However, these tests can sometimes give false positives or negatives, so they should be used alongside dietary tracking for best results.
If food sensitivities are a persistent issue, underlying gut infections (H. pylori, Candida, parasites) might be involved. A comprehensive stool test can provide insights into gut imbalances contributing to inflammation.
Once you’ve identified and removed trigger foods, the next step is healing your gut so your immune system can reset and function properly.
Adding anti-inflammatory, nutrient-dense foods can help repair the gut lining and support digestive health.
🍖 Bone Broth – Rich in collagen and amino acids that help heal the gut lining.
🥑 Healthy Fats – Avocados, coconut oil, and olive oil help reduce inflammation.
🥦 Non-Starchy Vegetables – Provide fiber and antioxidants to support gut health.
🍏 Fermented Foods – Sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir, and probiotic-rich foods restore beneficial gut bacteria.
If your digestion is weak, supporting it with digestive aids can help.
💊 Digestive Enzymes & HCL – Help break down proteins and improve nutrient absorption.
🌿 Ginger & Peppermint Tea – Reduce bloating, inflammation, and improve digestion.
Chronic stress can weaken gut health and worsen inflammation. Managing stress and prioritizing rest is key.
🧘 Practice relaxation techniques – Deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can lower stress levels.
😴 Get quality sleep – Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to allow the body to heal.
Chronic inflammation from food sensitivities is a silent but powerful driver of many modern health problems. However, the good news is that you control what you put into your body.
By identifying trigger foods through an elimination diet, healing your gut, and adopting an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, you can reduce inflammation, regain energy, and improve your overall well-being.
If you suspect food sensitivities are affecting your health, start with an elimination diet and consider working with a functional medicine practitioner for deeper gut testing and personalized support. Your body has an incredible ability to heal—give it the right tools, and it will!
Food allergies cause immediate and sometimes life-threatening reactions, while food sensitivities cause delayed and more subtle inflammatory responses.
It varies, but most people notice improvements within 4–8 weeks after eliminating trigger foods and healing their gut.
Some people can reintroduce foods in moderation after healing their gut, while others may need to avoid certain foods long-term.
Not necessarily—many gluten-free products contain processed ingredients that can still cause inflammation.
Look for multi-strain probiotics with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species to support gut health.
=======================
Recommended Products: