
Sleep is crucial to overall health, affecting physical recovery, cognitive function, emotional regulation, and immune resilience. However, many overlook how gut health and the gut-brain axis influence sleep quality. The relationship between sleep and gut health is a two-way street—disruptions in one can negatively impact the other.
By understanding this connection, individuals can make lifestyle, dietary, and functional medicine-based changes to enhance sleep quality and digestive health.
Sleep is far more than just a rest period—it is a time for the body to repair, regenerate, and balance essential functions. It supports:
When sleep is inadequate, it increases the risk of mood disorders, memory problems, weakened immunity, weight gain, and chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes. Poor sleep also contributes to chronic inflammation, a key factor in many health conditions, including gut dysfunction.
Functional medicine views sleep disruptions as a symptom of underlying imbalances rather than a condition to be treated in isolation. It considers multiple contributing factors, including gut health, nutrition, stress levels, inflammation, and exposure to environmental toxins.
A key focus of functional medicine is the gut-brain axis, which plays a significant role in sleep regulation. The gut microbiome influences the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and melatonin, both essential for healthy sleep patterns. An imbalanced gut can disrupt these neurotransmitters, leading to insomnia, poor sleep quality, and increased stress responses.
Functional medicine practitioners use a holistic, personalized approach to sleep improvement, incorporating:
This root-cause approach not only improves sleep but also enhances long-term health outcomes.
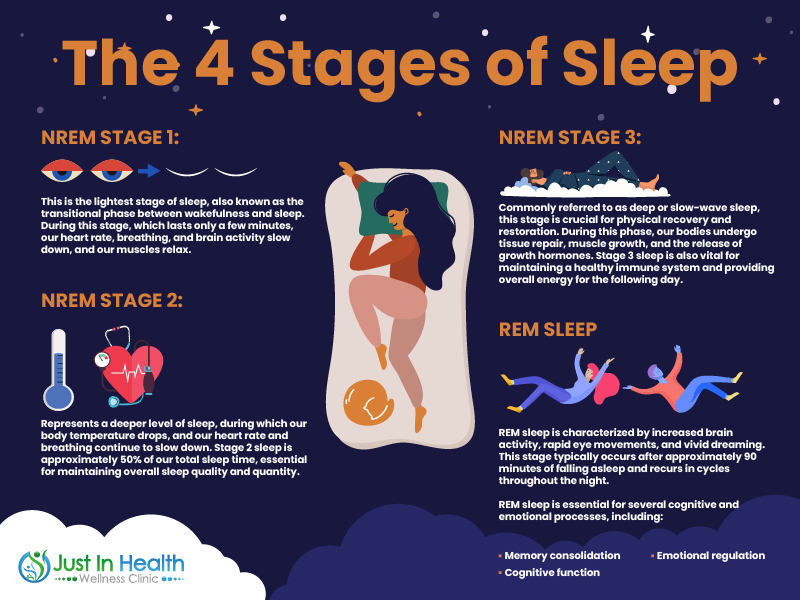
Sleep is divided into two major categories: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. These cycles repeat throughout the night, each playing a different role in physical and cognitive restoration.
Each sleep stage is vital for optimal health, and disruptions can lead to problems such as cognitive decline, weakened immunity, increased inflammation, and metabolic imbalances.
Sleep is essential for maintaining balance across multiple body systems.
Prioritizing sleep enhances brain function, emotional stability, immune resilience, and metabolic balance.
Several sleep disorders stem from underlying imbalances that functional medicine seeks to correct.
Addressing gut health, hormonal regulation, and inflammation can improve sleep quality naturally.
The gut microbiome plays a critical role in sleep quality by influencing neurotransmitter production, immune function, and inflammation levels.
Poor sleep also negatively impacts gut health, leading to:

Improving sleep naturally requires environmental, dietary, and lifestyle adjustments.
Certain nutrients and foods support sleep by enhancing neurotransmitter production and relaxation.
Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and heavy meals before bed improves sleep quality.
Functional medicine practitioners may recommend natural supplements to optimize sleep patterns.
It is always best to consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements.
Sleep is an essential pillar of health, influencing digestion, metabolism, brain function, and immune strength. Functional medicine treats sleep disturbances by addressing gut health, stress, inflammation, and hormone imbalances.
Individuals can improve sleep quality and overall well-being by adopting healthy sleep habits, optimizing nutrition, and managing stress.
How does gut health impact sleep?
The gut microbiome produces serotonin and melatonin, which regulate sleep. An unhealthy gut disrupts these processes, leading to poor sleep.
Can poor sleep cause digestive problems?
Yes, sleep deprivation increases stress hormones, weakens the gut lining, and disrupts microbiome balance, contributing to bloating and inflammation.
What foods improve sleep?
Magnesium-rich foods (almonds, spinach), tryptophan sources (turkey, nuts), and melatonin-rich foods (tart cherries) support sleep.
Does stress affect both sleep and gut health?
Absolutely. Chronic stress disrupts sleep cycles and gut microbiome balance, increasing inflammation.
What is the best natural remedy for sleep?
A combination of good sleep hygiene, gut-friendly nutrition, and stress reduction is the most effective strategy.
References:
“Why Sleep Matters — Healthy Sleep” by Harvard Medical School Division of Sleep Medicine
“The Role of Sleep in Cognition and Emotion” by Matthew P. Walker and Robert Stickgold
“The Impact of Sleep on Mental Health” by Dr. Michael J. Breus
“Sleep and Immune Function” by Luciana Besedovsky, Tanja Lange, and Jan Born
“Sleep and Hormonal Regulation in Health and Disease” by Dr. Eve Van Cauter and Dr. Karine Spiegel
“Insomnia: Pathophysiology and Implications for Treatment” by Dr. Daniel J. Buysse
“Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease” by Dr. Apoor S. Gami and Dr. Virend K. Somers
“Circadian Rhythms and Sleep: Impact on Bodily Functions” by Dr. Eve Van Cauter and Dr. Karine Spiegel
“Nutrition and Sleep: Roles in Obesity and Metabolic Health?” by Dr. Marie-Pierre St-Onge and Dr. Arindam RoyChoudhury
“Exercise, Sleep, and Cognition: Interactions in Aging” by Dr. Kelly R. Evenson and Dr. David X. Marquez