
Gluten sensitivity affects millions worldwide, yet it is often misunderstood. Unlike celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder, gluten sensitivity does not damage the small intestine but can still cause digestive issues, fatigue, and other health symptoms.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to gluten sensitivity, covering key differences from celiac disease, common symptoms, underlying causes, and treatment strategies, including dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle modifications.
Gluten sensitivity, or non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), is a condition where the body negatively reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley.
Unlike celiac disease, gluten sensitivity does not cause intestinal damage, but it can still lead to digestive discomfort, neurological symptoms, and inflammation.
Although celiac disease and gluten sensitivity share similar symptoms, they are fundamentally different conditions.
| Feature | Celiac Disease | Gluten Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune reaction to gluten | Non-autoimmune reaction to gluten |
| Intestinal Damage | Yes, damages small intestine | No intestinal damage |
| Symptoms | Digestive issues, nutrient malabsorption, fatigue, skin rashes, joint pain | Bloating, brain fog, headaches, joint pain, fatigue |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, biopsy of small intestine | No specific test; diagnosed through elimination diet |
| Severity | Can lead to severe health complications like anemia, osteoporosis, infertility, and increased cancer risk | Causes discomfort but no long-term intestinal damage |
Another condition often confused with gluten sensitivity is wheat allergy, a severe allergic reaction to wheat proteins that can cause anaphylaxis.
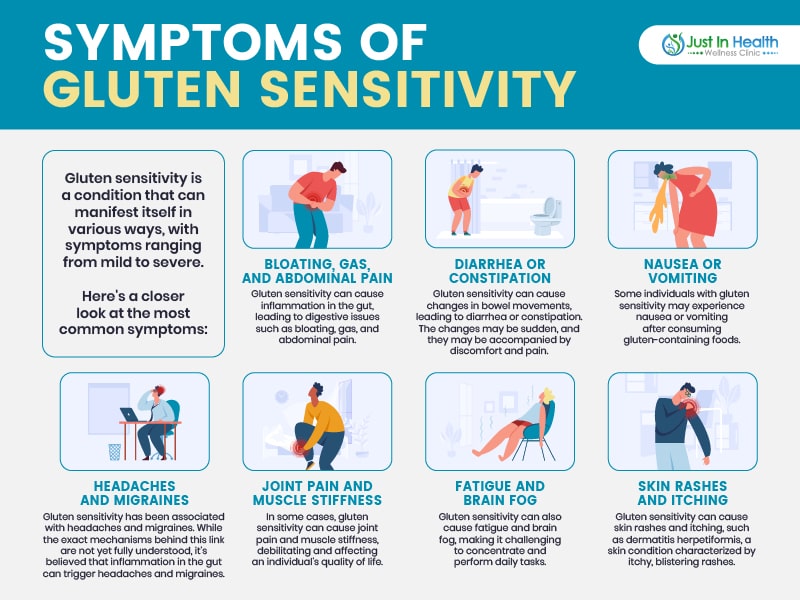
Symptoms of gluten sensitivity vary widely and can affect multiple systems in the body.
Common Symptoms Include:
Not everyone experiences all symptoms; some may have mild reactions while others struggle with severe discomfort.
The exact cause of gluten sensitivity is still being researched, but several factors may contribute to its development.
Studies suggest that imbalances in gut bacteria and increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”) may play a role.
People with gluten sensitivity often react to other foods, such as:
This suggests multiple food sensitivities may overload the immune system, leading to widespread inflammation and symptoms.
Unlike celiac disease, there is no definitive medical test for gluten sensitivity. Diagnosis is usually done by:
The most effective treatment for gluten sensitivity is adopting a gluten-free diet and addressing gut health.
A gluten-free diet requires avoiding foods that contain wheat, rye, and barley, including:
❌ Bread, pasta, cereals, baked goods
❌ Beer, malt beverages
❌ Soy sauce, processed snacks, dressings
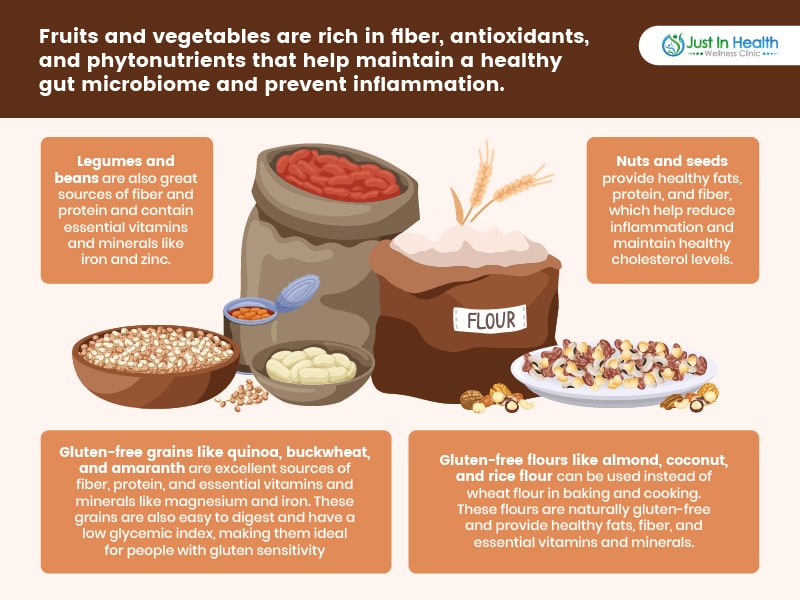
Instead, focus on whole, naturally gluten-free foods, such as:
✅ Fruits & Vegetables – Rich in fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients.
✅ Legumes & Beans – Excellent sources of protein and fiber.
✅ Nuts & Seeds – Provide healthy fats and essential minerals.
✅ Gluten-Free Grains – Quinoa, buckwheat, amaranth, rice, millet.
✅ Plant-Based Protein Sources – Lentils, chickpeas, tofu (gluten-free certified).
Certain supplements can help manage gluten sensitivity by reducing inflammation and supporting digestion.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting new supplements.

Managing gluten sensitivity goes beyond diet. Stress management, exercise, and sleep hygiene can enhance gut health and well-being.
Gluten sensitivity can be challenging, especially for those following a vegan or plant-based diet, but managing symptoms is possible with proper dietary adjustments, gut support, and lifestyle changes.
If you suspect gluten sensitivity, consult a functional medicine practitioner to create a personalized treatment plan.
References: