The Science of Inflammation: How to Identify and Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Introduction
Inflammation is a natural part of the body’s immune response, designed to protect and heal tissues after injury or infection. Acute inflammation, like redness and swelling from a cut, is a short-term process essential for recovery. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can quietly wreak havoc on your health. Chronic inflammation has been linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and even certain cancers.
Understanding the science behind inflammation and adopting strategies to manage it can empower you to improve your well-being. Let’s dive into the causes, signs, and practical steps to reduce chronic inflammation and boost your overall health.
The Science Behind Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex biological response to harmful stimuli like infections, toxins, or physical injuries. It involves immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators working together to remove threats and begin healing.
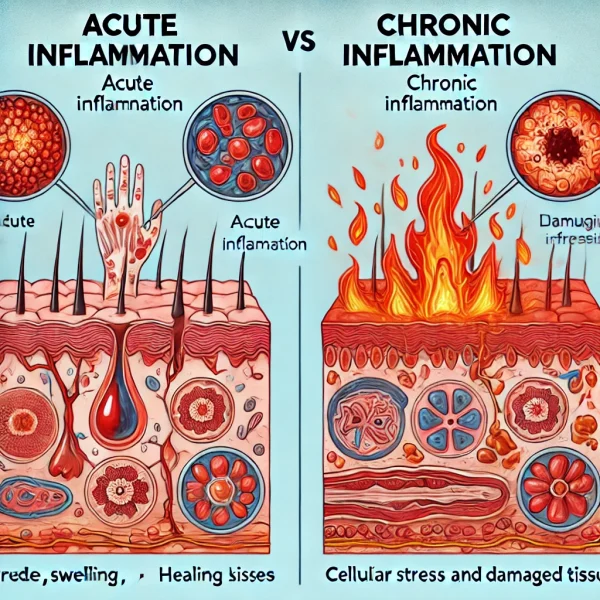
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
- Acute inflammation is rapid, lasting from a few hours to days, and is typically visible (e.g., redness or swelling).
- Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, persists for months or even years. It can result from ongoing exposure to irritants, an overactive immune system, or unresolved acute inflammation.
Common Triggers of Chronic Inflammation
- Poor diet (high in sugar, processed foods, and trans fats).
- Stress and lack of sleep.
- Toxins from pollution or household chemicals.
- Infections (e.g., untreated gut imbalances like dysbiosis).
Over time, chronic inflammation can damage tissues, impair organ function, and lead to systemic health issues.
Signs of Chronic Inflammation
Recognizing the signs early can help prevent long-term damage. Some common indicators include:
- Persistent fatigue.
- Digestive problems like bloating or IBS.
- Joint pain or stiffness.
- Skin issues (e.g., acne, eczema).
- Brain fog or memory problems.
- Frequent infections.
How Chronic Inflammation is Diagnosed
Doctors may use biomarkers to assess inflammation levels, including:
- C-reactive protein (CRP): Elevated levels indicate systemic inflammation.
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6): A key inflammatory cytokine linked to immune dysfunction.
Steps to Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Tackling chronic inflammation requires a multifaceted approach. Here are science-backed strategies:
1. Dietary Changes
Your diet plays a pivotal role in managing inflammation.
- Include anti-inflammatory foods:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (found in salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts).
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale).
- Spices like turmeric and ginger.
- Fruits such as berries and citrus.
- Healthy fats (extra virgin olive oil, avocado).
- Avoid pro-inflammatory foods:
- Refined sugars, processed snacks, and trans fats.
- Excessive alcohol and artificial additives.
2. Lifestyle Habits
Simple changes in your daily routine can reduce inflammation:
- Exercise regularly: Aim for 30 minutes of moderate activity (e.g., walking, swimming).
- Stress management: Incorporate meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
- Sleep quality: Ensure 7–9 hours of restful sleep per night. Poor sleep is closely linked to higher CRP levels.
3. Key Supplements for Inflammation
- Curcumin: The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, has powerful anti-inflammatory effects and reduces oxidative stress.
- Omega-3s: Found in fish oil, these fatty acids lower inflammation and improve heart health.
- Resveratrol: This antioxidant, found in grapes and red wine, has been shown to reduce inflammatory markers.
- NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine): Boosts glutathione levels, a critical antioxidant that helps neutralize inflammation at the cellular level.
Natural Remedies and Practices
In addition to dietary and lifestyle changes, these remedies can support inflammation reduction:
- Sinus Flush: Using a saline solution, this practice clears nasal passages and prevents inflammation from allergens or infections.
- Herbal Teas: Chamomile, ginger, and green tea are anti-inflammatory beverages.
- Detoxification: Practices like dry brushing and Epsom salt baths can help reduce toxin-related inflammation.
- Sauna Therapy: Regular sauna use promotes detoxification and reduces inflammatory markers.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation doesn’t have to define your health. Identifying the triggers and incorporating anti-inflammatory strategies into your lifestyle can improve your well-being and protect against long-term health issues. Start with small changes, like enhancing your diet with whole foods, reducing stress, and adding key supplements to your routine.
=======================
Recommended Products:
Omega Supreme 120 caps
Curcumin Supreme 60 caps

